Understanding Electric Demand
What is Electrical Demand?
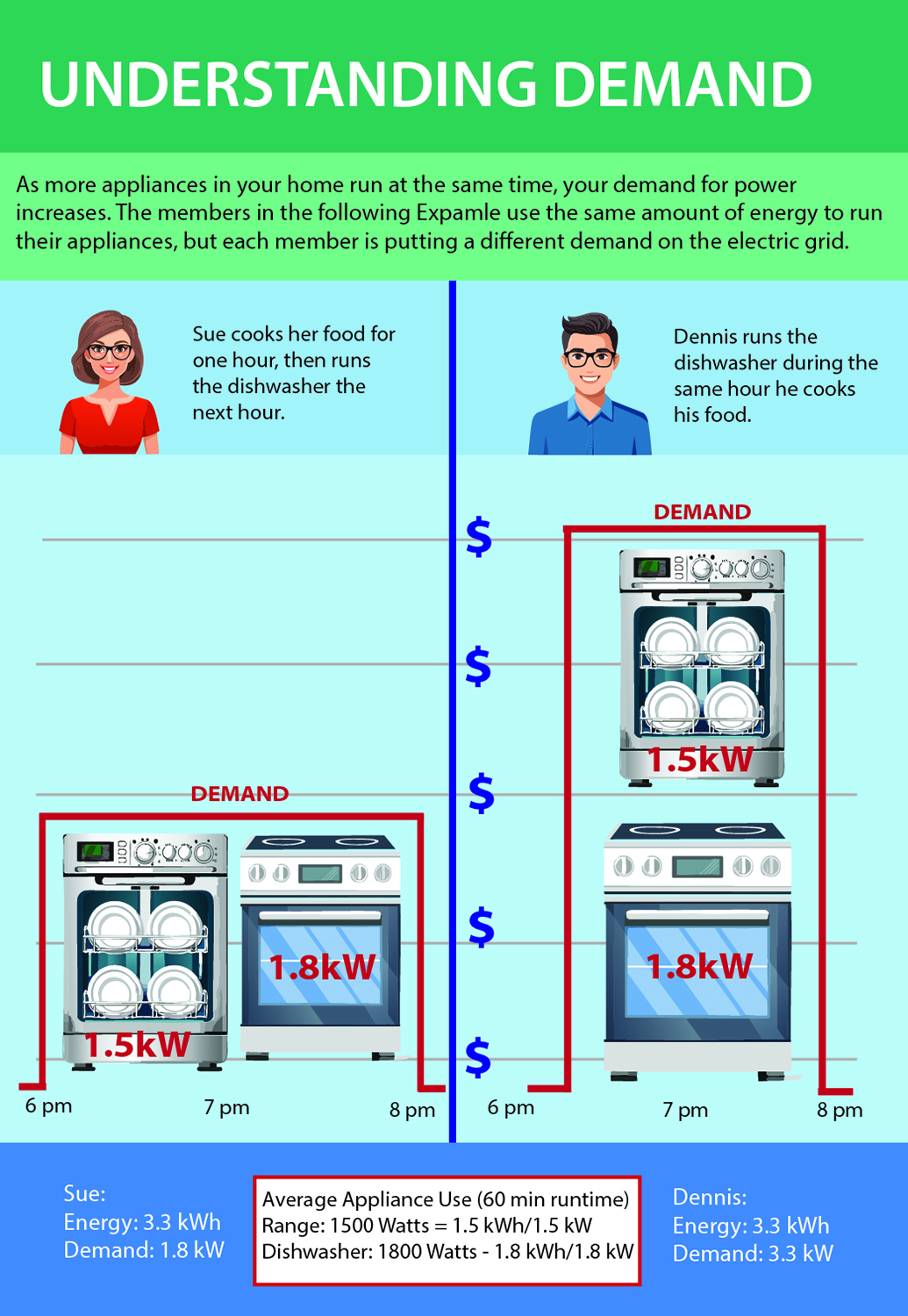
Electric demand refers to the amount of electrical power members require at any given time. It is a critical aspect of energy management and is measured in kilowatts (kW). Understanding electric demand helps cooperatives plan their energy supply, maintain system reliability, and provide affordable rates to their members.
How is Demand Calculated or Determined?
Demand is measured in kilowatts and not in kilowatt hours. A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a unit of energy, and it represents the amount of electricity used over time. On the other hand, demand refers to the instantaneous power consumption at any given moment, typically measured in kilowatts (kW). For better understanding let’s use an example of a water heater. The water heater has a power rating of 3 kW. This means that it consumes 3 kilowatts of power while operating. For this given day, the water heater ran for 2 hours. Power = 3 kW (demand) and Time = 2 hours. To calculate energy consumption the following equation is used: Energy (kWh) = 3 kW X 2 hours = 6 kWh. Demand (3 kW) is the instantaneous power that the water heater draws when it is on. Energy consumption (6 kWh) is the total energy used by the water heater when it operates for two hours.
What Benefit Does the Cooperative Receive by Charging the Member Demand?
The more members that manage their demand, less is needed to secure more generation and build facilities such as transmission lines, substations, etc. Managing the growing demand will help keep rates low. By understanding your peak demand, you can better manage your electrical usage.
How Can a Member Reduce Their Demand?
The best way to reduce demand is to consider how and when you use all electric devices in your home or business. Spreading out the time you use electrical
devices will help lower demand.